Measure your biological age with a simple finger prick test.
What is the GlycanAge test and why is it useful?
Why do you need a test?
The data is unequivocal that a healthy lifestyle can confer 10 years of extra active life to a population. The question is how are you personally doing? If you change your lifestyle, are you combatting the inflammation and degenerative processes that constitute aging?
To see where you are and monitor progress you need a chemical marker. Glycosylation of the protein Immunoglobulin G [IgG], is a useful marker of inflammation: abnormal patterns can predict various disease processes.
How does GlycanAge test biological age?
The test profiles glycosylation of IgG], which is a useful marker of biological age ie how worn out the body is.
‘Glycosylation’ is the pattern of sugars attached to the IgG molecule. These sugars modulate the function of the protein – indeed the protein cannot function without them. and the pattern reflects the extent of bodily inflammation and as such is a close marker of many disease processes. It can be used as a successful ‘early warning system’ predicting some cancers, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and Alzheimer’s ahead of conventional screening tools. This is a separate issue to protein ‘glycation’ [as in the marker of sugar control HbA1c] – glycation is protein damage, glycosylation is a controlled physiological process.
If your biological age is well below your chronological age, then you are likely to live to 100; and because of low levels of inflammation have a long ‘HealthSpan’ ie few life-spoiling diseases or time in a care home in your last decade of life.
Conversely, if your biological age is advanced beyond your chronological age then [if you do nothing] you may die prematurely, and the end of your life will likely be of very poor quality.
The unique individuality of this measure
Each person has a specific signature profile of different N-glycan structures attached to the IgG molecule that varies according to the health of that body.
Here is the individual pattern, for 6 individuals. Each colour represents a N-glycan option and the different percentages are shown1.
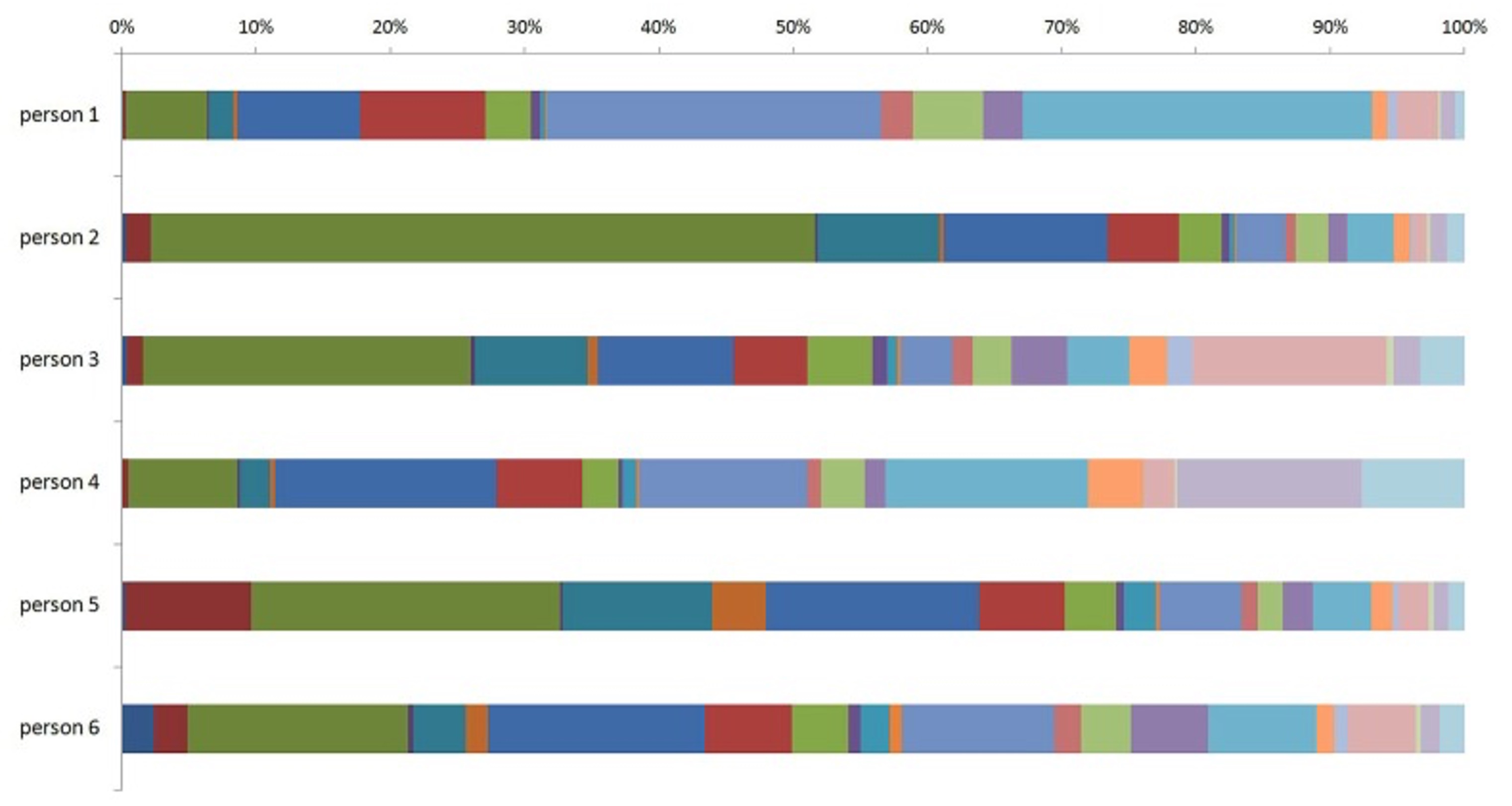
You can see how each profile varies significantly
This profile is a biomarker of the effects of ‘ageing’[i], [ii]. Its usefulness comes in three ways: first if it shifts to a better pattern when inflammation is lower than usual for age, this is indication of an individual who is likely to become a centenarian
Second, if there is a worse pattern ie inflammation higher than usual, this correlates with premature death, autoimmune disease, cardiovascular risk, cancer probability in various sites and the likelihood of diabetes
[i] Krištić J, Lauc G, Pezer M. Immunoglobulin G glycans - Biomarkers and molecular effectors of aging. Clin Chim Acta. 2022 Aug 12;535:30-45. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2022.08.006. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 35970404.
[ii] Krištić J, et al.. Glycans are a novel biomarker of chronological and biological ages. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014 Jul;69(7):779-89. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glt190. Epub 2013 Dec 10. PMID: 24325898; PMCID: PMC4049143.
How are the Glycan Age results presented?
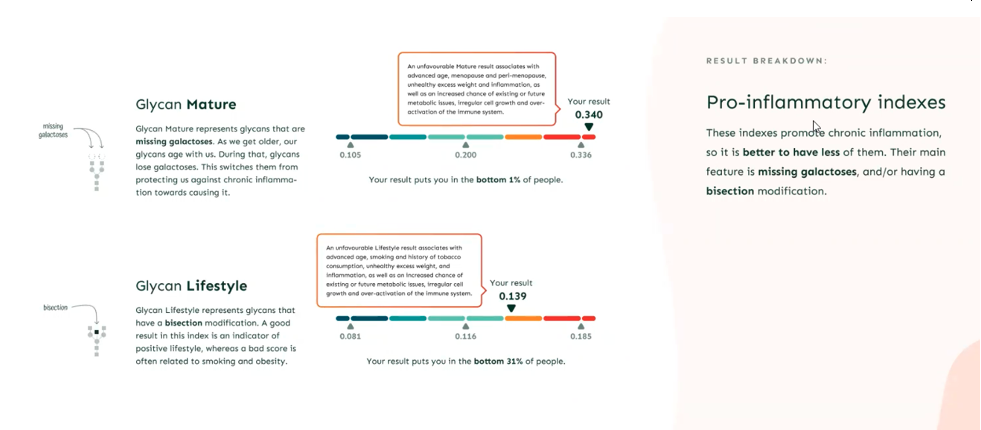
There are 5 variations in glycosylation that can be predictive of inflammaging and cardiometabolic disease. [eg Heart attack, stroke, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, diabetes and Alzheimer’s dementia.].
The results are presented as shown below - there are 5 aspects of the profile, 3 anti-inflammatory and 2 pro-inflammatory measures shown on a scale from bad to good or vice versa..

Can you reverse an abnormal pattern?
Yes: lifestyle modification or in eg ulcerative colitis, specific treatment, can reverse that pattern[i] and success be demonstrated on re-test. Poor patterns in women, perimenopausally, are reversed by HRT[ii].
What is the test?
This is a fingerprick blood sample. It has to be measured in a specialised laboratory outside the UK and is done in batches so the result takes 3-4 weeks.
For those interested - Research into IgG glycosylation and disease
Cancer
Abnormal glycosylation patterns are seen in brain tumours[iii], may be a potential future marker for early breast cancer[iv] are increased in the urine of patients with gastric cancer, pancreatic cancer, cholangiocarcinoma and colorectal cancer [CRC][v]. In CRC, N-glycosylation is potentially a novel prognostic biomarker[vi]. In both small cell and non-small cell lung cancer targeting the protein N-glycosylation of cancer small extracellular vesicles (sEVs or exosomes) may allow detection and characterisation of cancer types and their origins, as well as developing therapeutic strategies[vii].
Inflammatory disease
Abnormal IgG glycosylation is seen in ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease. The markers decline during successful treatment[viii].
Glycan Age and menopause
These results suggest that IgG glycans and consequently also the glycan age are under strong influence of gonadal hormones and that estradiol therapy can prevent the increase of glycan age that occurs in the perimenopausal period[ix].
The science of the test.
What are glycans
Glycans are complex carbohydrates that have an important role if how the body adapts DNA function without modifying the DNA template. Lauc et al say[x].:
Our hypothesis is that the invention of glycans was the third revolution in evolution (after the appearance of nucleic acids and proteins). This enabled novel molecular entities that do not need the direct genetic template that proteins and nucleic acids require. Glycans are an epigenetic mechanism that enables adaptive response to environmental changes, and, unlike other epiproteomic modifications, which act as off/on switches, glycosylation significantly enables novel functions. The importance of glycosylation is evident from the fact that nearly all proteins invented after the appearance of multicellular life are composed of both polypeptide and glycan parts.[xi].
How do they work?
Glycans modulate cellular responses10
.
Surfaces of all eukaryotic cells are covered with a thick layer of complex glycans attached to proteins or lipids. Many cells in our organism can function without the nuclei, but there is no known living cell that can function without glycans on their surface. Anything approaching the cell, being it a protein, another cell, or a microorganism, has to interact with the cellular glycan coat
In some biological systems, like for example AB0 blood groups, glycans act as simple molecular switches that introduce inter-individual variability of cellular surfaces. In other systems, like immunoglobulin glycosylation, they enable new physiological functions, which could not be performed without this complex post-translational ie post DNA level, tool. Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is an excellent model glycoprotein because its glycosylation has been well defined and many important functional effects of alternative IgG glycosylation have been described For example, glycosylation acts as a switch between pro- and anti-inflammatory IgG functionality.
The GlycanAge index combines one nongalactosylated glycan (GP6) and two digalactosylated glycans (GP14 and GP15). This index predicts chronological age in the well, and importantly explains 58% of variation in chronological age and sex. This is impressive compared with other so-called age biomarkers like telomere length where most studies show 15%–25%. After correcting for chronological age, the GlycanAge index correlates strongly with physiological parameters associated with measurements related to biological age[xii]
[i] Štambuk J, et al. Distinct Longitudinal Changes in Immunoglobulin G N-Glycosylation Associate with Therapy Response in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 30;23(15):8473. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158473. PMID: 35955616; PMCID: PMC9368836.
[ii] Jurić J, et al. Effects of estradiol on biological age measured using the glycan age index. Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Oct 13;12(19):19756-19765. doi: 10.18632/aging.104060. Epub 2020 Oct 13. PMID: 33049709; PMCID: PMC7732334.
[iii] Veillon L, Fakih C, Abou-El-Hassan H, Kobeissy F, Mechref Y. Glycosylation Changes in Brain Cancer. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2018 Jan 17;9(1):51-72. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00271. Epub 2017 Nov 7. PMID: 28982002; PMCID: PMC5771830.
[iv] Gebrehiwot AG, er al. Exploring serum and immunoglobulin G N-glycome as diagnostic biomarkers for early detection of breast cancer in Ethiopian women. BMC Cancer. 2019 Jun 17;19(1):588. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5817-8. PMID: 31208374; PMCID: PMC6580580.
[v] Hanzawa K, et al. Increased levels of acidic free-N-glycans, including multi-antennary and fucosylated structures, in the urine of cancer patients. PLoS One. 2022 Apr 12;17(4):e0266927. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0266927. PMID: 35413075; PMCID: PMC9004742.
[vi] Theodoratou E, et al. Glycosylation of plasma IgG in colorectal cancer prognosis. Sci Rep. 2016 Jun 15;6:28098. doi: 10.1038/srep28098. PMID: 27302279; PMCID: PMC4908421.
[vii] Kondo K, et al. Identification of distinct N-glycosylation patterns on extracellular vesicles from small-cell and non-small-cell lung cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;298(6):101950. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101950. Epub 2022 Apr 18. PMID: 35447118; PMCID: PMC9117544.
[viii] Štambuk J, et al. Distinct Longitudinal Changes in Immunoglobulin G N-Glycosylation Associate with Therapy Response in Chronic Inflammatory Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 30;23(15):8473. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158473. PMID: 35955616; PMCID: PMC9368836.
[ix] Jurić J, et al. Effects of estradiol on biological age measured using the glycan age index. Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Oct 13;12(19):19756-19765. doi: 10.18632/aging.104060. Epub 2020 Oct 13. PMID: 33049709; PMCID: PMC7732334.
[x] Lauc G, Krištić J, Zoldoš V. Glycans - the third revolution in evolution. Front Genet. 2014 May 23;5:145. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00145. PMID: 24904645; PMCID: PMC4033155.
[xi] Lauc G, Krištić J, Zoldoš V. Glycans - the third revolution in evolution. Front Genet. 2014 May 23;5:145. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2014.00145. PMID: 24904645; PMCID: PMC4033155.
[xii] Krištić J, et al. Glycans are a novel biomarker of chronological and biological ages. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2014 Jul;69(7):779-89. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glt190. Epub 2013 Dec 10. PMID: 24325898; PMCID: PMC4049143.
If you would like to book a test here's how.
Our Partner delivers the kit to your door at the address you provided and we send a secure payment link to you to make the payment
-
One test order - £289.00
-
Two test order - £492.00
When you receive your test kit…
Please
1. Do the test Monday -Thursday to minimise postal delays.
2. Post at a post office not in a remote box that may not be emptied every day.
3. Be aware that the main lab for this test world wide is in Croatia so your package has to travel.
4.Results take around 4 weeks depending on any postal delays in the UK [strikes etc]
Once we have the results back we will provide you with a report like the one below
Please complete the form to start your order
© Copyrights by Your Company. All Rights Reserved.
